What is power transmission and transformation?
The transmission of current often leads to loss due to the heat of the line, so the voltage is increased through transformers during transmission, so that the current becomes smaller to reduce heat loss. High-voltage electricity is very dangerous, and the target electrical appliances do not need such a high voltage, so it is necessary to reduce the voltage through power transformation. Since multiple power transformations are required in the process of current transmission, the transmission of current is called power transmission and transformation.
Power transmission and transformation is the transmission of power from the power plant to the grid. It increases the low voltage (such as 500,000 volts) for remote transmission. The higher the voltage of the same power, the smaller the current, and the smaller the current, the smaller the loss on the line.
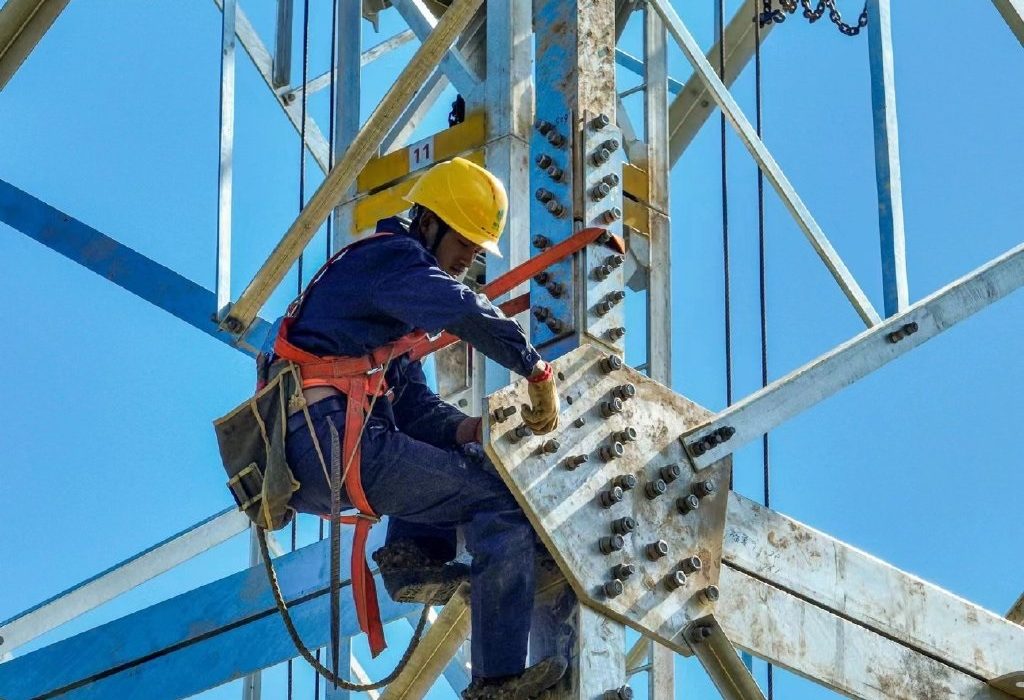
Generally, in the power industry, 35kV~1000kV is called power transmission and transformation, and 10kV and below is called distribution network. Power transmission and transformation can be simply divided into two main parts: 1. Transmission lines. 2. Substation. Generally, the voltage sent from the power plant is relatively low. If it is not boosted, then according to the ratio of AC UI, the current on the line will be relatively large. Since the heating of the line is related to the resistance and current, the greater the current, the greater the current generated by the same wire. The heat is also relatively large, so most of the electricity from the power plant will be lost on the wires. In addition, the higher the heat of the wire, the greater the harm to the wire. In order to avoid the above adverse effects. The measure is to increase the voltage and reduce the current. So a booster station is needed. Generally, the first stop of the electricity from the power plant is the step-up substation (low voltage in, high voltage out). Substations generally have step-up stations and step-down stations, and the voltage levels are generally from small to large: 35kV, 110kV, 220kV, 500kV, 1000kV. It is a part of the power system, and its function is to transform the voltage level, collect and distribute electric energy, mainly including transformers, busbars, line switchgear, buildings and facilities required for power system safety and control. Substations generally divide the service range according to the voltage level, and the larger the voltage level, the larger the service radius of the substation. Our country currently has the only AC 1000kV substation in commercial operation in the world with independent intellectual property rights, and 500kV substations are now relatively common. The power system has been relatively developed.
Power transmission and transformation is like a large network covering the whole country. A substation is a node in the network. Connecting each node is the transmission line, and the transmission line can be divided into: steel tower, steel pipe pole, concrete pole, power cable and other forms. The comparison in the form of iron towers can be seen everywhere on both sides of the expressway. With the development of science and technology and the strength of the country, the power cables with high cost are slowly being applied, which is the practice of turning from the sky to the ground. It embodies the progress and civilization of the society.